In the paper “Thumbs up? Sentiment Classification using Machine Learning Techniques.”, Pang et al introduced the idea of sentiment analysis using a Naïve Bayes classifier. The key idea is to combine the probability of occurrence of the words in positive and negative sentiment reviews, probability of occurrence of the words across all reviews, probability of occurrence of positive or negative reviews across all reviews to determine the probability of a text being a positive or negative based on the words in the text.
Month: January 2023
Text Similarity
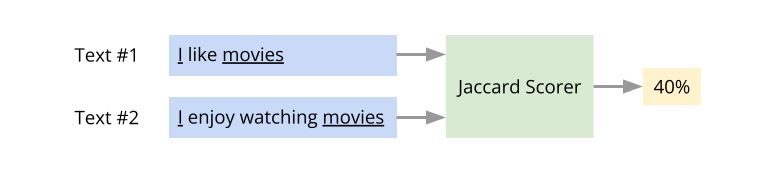
Here is a super-short intro to the concept of text similarity. There are many ways to quantify the similarity between two pieces of text. One popular approach is to use what is known as the Jaccard similarity. Consider these two sentences:
- I like movies
- I enjoy watching movies
The number of words that occur in both the sentences is two (“I”, “movies”). The total number of unique words across the two sentences is five (“I”, “like”, “movies”, “enjoy”, “watching”). Here, the Jaccard similarity score = 2/5. That is, 40% similarity. The idea of text similarity is has several applications. For example, given a question and a collection of sentences that are potential answers to the question, the most likely answer to the question is the one with the highest similarity score.
Text Entailment Using RoBERTa
Here is a super-simple implementation for solving Text Entailment using RoBERTa pre-trained model.
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("roberta-base")
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("roberta-base")
def analyze(pr, hy): # pr is premise, hy is hypothesis
inputs = tokenizer.encode(pr, hy, return_tensors='pt')
outputs = model(inputs)
label = outputs[0].argmax().item()
if label == 0: return "contradiction"
elif label == 1: return "entailment"
else: return "neutral"
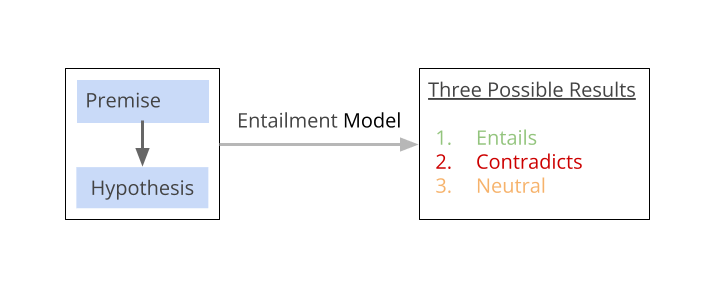
Text Entailment Problem
Text entailment is a problem in NLP (Natural Language Processing). Here the task is to determine if one piece of text, (aka premise) logically implies another piece of text (aka hypothesis). There are three possible outcomes from a Text Entailment analysis. The hypothesis may be entailed, contradicted or neutral with respect to the premise.
For example, consider the premise: “The elephant is trumpeting”, and the hypothesis: “The elephant is making noise”. In this example, the hypothesis “The elephant is making noise” can be logically inferred from the premise “The elephant is trumpeting”. So, the relationship between the premise and the hypothesis is “entailment”.
Large Language Model
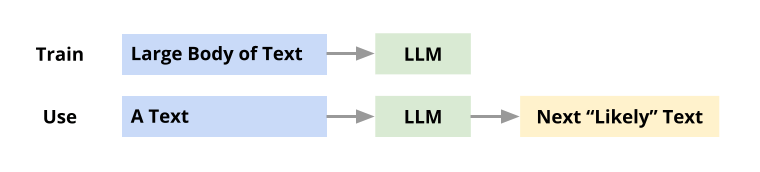
A Large Language Model aka LLM is a Machine Learning model trained with massive amounts of text. Using the “knowledge” gained from training, this model can generate new text, for any given prompt, You can think of it as a student who has read many books and can write an essay on any topic that you ask him or her to write about. In 2017, a new deep neural architecture called Transformer was invented by researchers. This architecture is the key breakthrough that resulted in powerful LLMs.